How Is Collagen Made, What Makes It, & How Is It Produced in the Body?

It's no secret that collagen is the most important ingredient in healthy, youthful skin. Some even hail collagen supplements and treatments as the next "fountain of youth." But have you ever wondered where this supposedly magic protein comes from?
You'll find it in certain foods, supplements, and serious skin care products, but it all starts in your own body. Collagen is a protein that your body naturally builds and creates on its own, giving strength and structure to many of your essential organs and connective tissue. With age comes a slowing down of the collagen-making process, resulting in a deficit that causes skin aging, joints weakening, and much more.
The collagen you'll find in supplements and products comes from external sources, namely animal and fish byproducts. The collagen in these products is extracted from animal and marine sources and then processed in order to transform the protein into something your body can absorb and use.
In this article, we'll explain where collagen occurs naturally, how your body makes it, and how the collagen in your products and supplements is made.
Where Is Collagen Found?
Collagen is the most abundant and important protein in your body, making up about 30% of its protein composition. There are 28 types of collagen, but the predominant types of collagen in the human body are types I, II, and III. 1
Let's take a closer look at where this protein is found:
Skin
Collagen plays an essential role in your skin, as it forms the foundational structure that keeps your skin supple and taut. In fact, collagenous fibers make up approximately 80% of your dermis, making it the most plentiful protein in your skin.
It works with elastin and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) to support skin elasticity and keep your skin strong and resilient to daily wear and tear. Collagen also plays a key role in wound healing. As we age, a natural loss of collagen shows most visibly on our skin, resulting in wrinkles and sagging. The collagen in your skin is mostly collagen type 1.

Connective Tissues (Bones & Cartilage)
Type 2 collagen is absolutely essential to your joint and bone health. It provides strength and structural support to your cartilage, which is a connective tissue that's hugely important to your joint health. The collagen made in your cartilage creates a strong yet flexible cushion layer to absorb shock and allow your bones to move without friction.
Muscle Tissues
You'll also find collagen in your muscle tissues, where it forms between 1–10% of your muscle mass. Some studies suggest that boosting your collagen production with supplements may help improve muscle growth after a workout. 3
Arteries
Collagen is also an important element in your heart health, as it forms the structure of your blood vessels and artery walls. This function is essential to a healthy blood flow and supply of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. 4

How is Collagen Made in the Body?
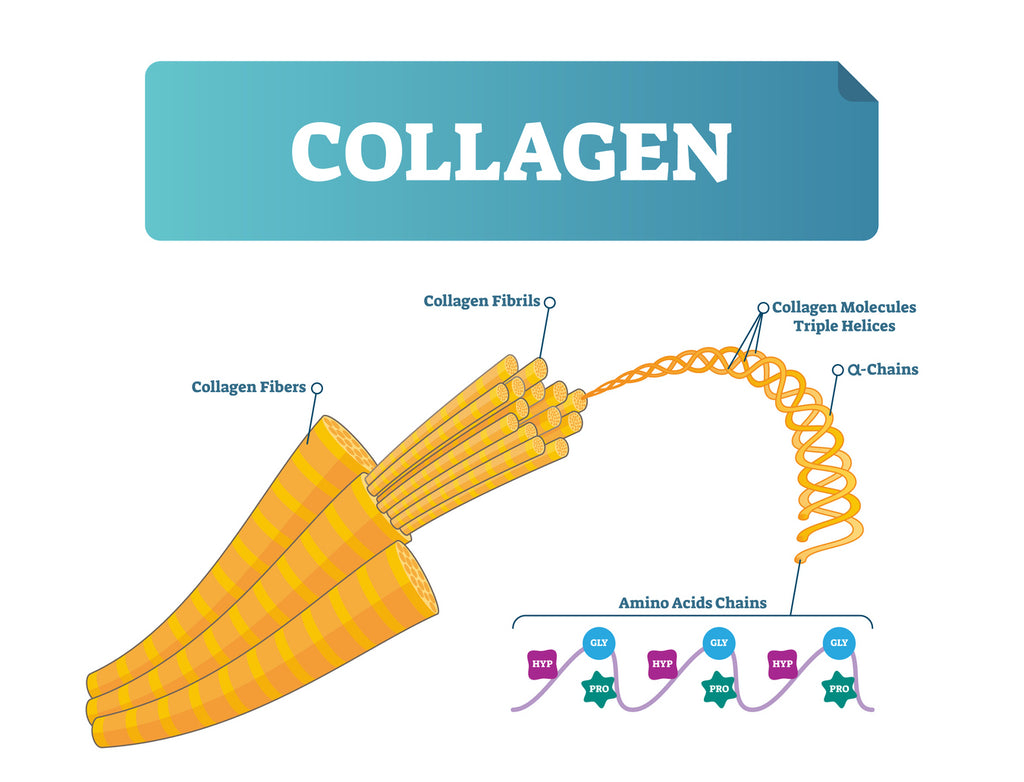
A collagen protein molecule is composed of a chain of amino acids that have been twisted into a triple helix structure. The collagen in your body is made through a process known as collagen synthesis.
Collagen synthesis begins in specialized cells called fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are the cells responsible for making collagen proteins. They exist in a structural layer known as an extracellular matrix.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a network of cells, proteins, and other molecules that gives structure to various tissues in the body. It's basically a foundational layer for many tissues like your skin or your cartilage, and it hosts fibroblasts alongside collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans like hyaluronic acid.
In the ECM, your fibroblasts synthesize a number of ingredients into collagenous fibers, twisting them into chains that come together to form a triple helix structure.
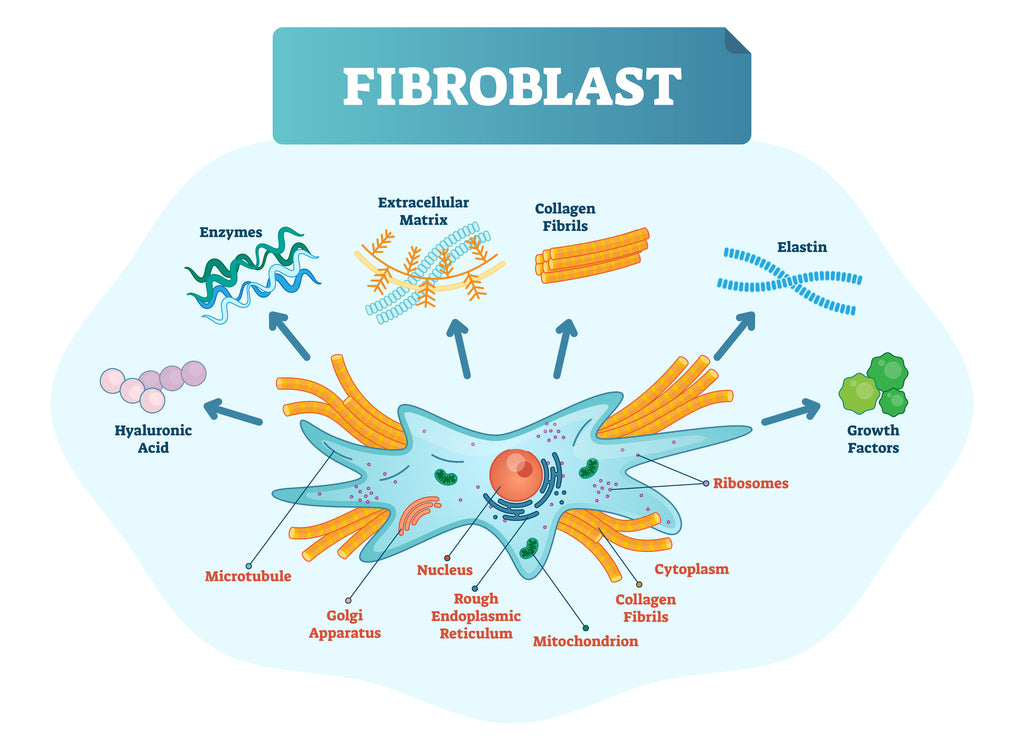
The 4 Elements of Collagen Synthesis
For collagen synthesis to work, your body needs four key ingredients. Let's take a closer look:
1. Amino Acids
First up, the two amino acids you need to know about when it comes to collagen production are glycine and proline.
Glycine is the most simple amino acid, and it is an element in many proteins. Glycine is the main amino acid involved in collagen synthesis, and it makes up about 35% of the collagen in your body. 2
Proline is another common amino acid and a building block for many proteins. It is essential to collagen production on its own, as well as in its oxidized state: hydroxyproline.
Collagen molecules are made up of polypeptide chains, which are chains made up of three amino acids in a sequence. This amino acid sequence is glycine followed by an alternating combination of proline and/or hydroxyproline.
2. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a crucial element in collagen synthesis. It activates enzymes that oxidize proline into hydroxyproline, which is needed to complete collagen's chain structure.
This nutrient also functions as a potent antioxidant, which stabilizes the proteins and protects them against degradation by harmful free radicals.
3. Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that plays an essential role in cellular repair, including your fibroblasts. Zinc protects your fibroblasts against damage during the synthesis process.
4. Copper
Copper is the final crucial element for collagen synthesis. Copper is a mineral that activates an enzyme in your body called enzyme lysyl oxidase, which is needed to form collagen as well as elastin fibers.
Once your body has enough amino acids, vitamin C zinc and copper, your fibroblasts get to work creating collagen. It starts by assembling amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline into chains, then twisting three amino acid chains into a triple helix – which you can picture as a braid-like structure. These triple helix structures come together to form a collagen fiber, which provides strength, structure, and support to your skin, connective tissue, and more!
External Sources of Collagen
Now that you know how collagen in your own body is made, you might be wondering where the collagen in your supplements and skincare products comes from.
Collagen is not only the most abundant protein in the human body, it is also an important protein found in animals like cows, chickens, and pigs, as well as in fish. This protein is often extracted in order to create skincare products or health and beauty supplements that help boost the human body's natural collagen production process. Let's take a closer look at where your beauty products come from:
Animal Collagen
Animal collagen comes from bovine, porcine, or chicken sources. Bovine (beef) collagen is a popular option in the beauty and skincare world as it is rich in type I and type III collagens. Chicken collagen, on the other hand, is particularly rich in type II, making it the best option for relieving joint pain.
Marine Collagen
Marine collagen is a type that has been derived from sea life. It is most commonly taken from the skin and scales of cold sea fish. It is the richest source of type I collagen, and it also is superior to animal sources when it comes to bioavailability i.e. the rate at which it can be digested. Because marine collagen molecules have a lower molecular weight than animal collagens, it is much easier to digest and can work quickly and effectively in the body – making it the premium choice for skincare and beauty products.
Plant-Based Collagen
Unfortunately, collagen is not found in plants, so a vegan or vegetarian diet is often not compatible with typical collagen supplements and products. There are, however, some options being developed that derive collagen-like substances from yeast and bacteria.
How Is Animal & Fish Collagen Made?
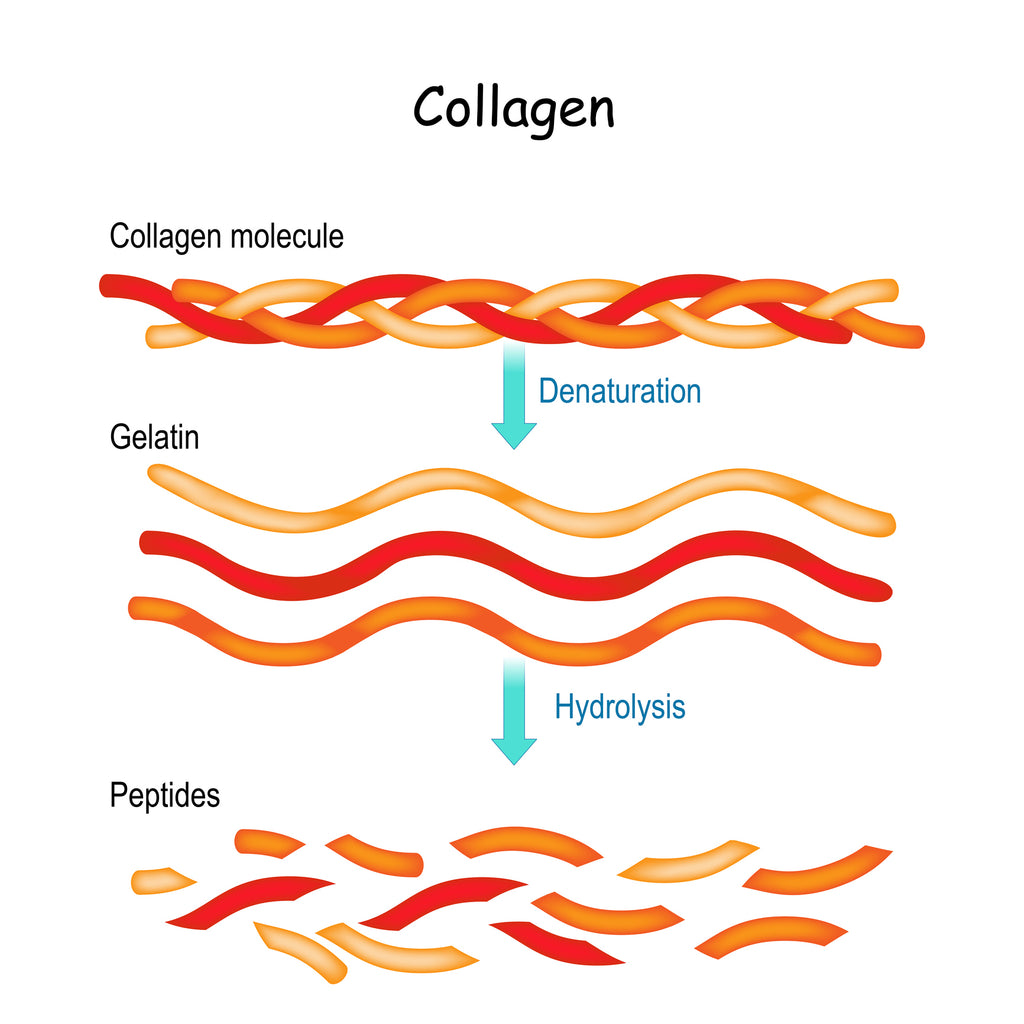
In its natural state, the collagen molecule is too large to be absorbed or digested into the human body. It needs to be broken down by hydrolysis into smaller nano-sized pieces to be digested and used.
Animal and marine collagens are typically extracted by boiling down the bones and connective tissue (i.e. animal/fish parts that are typically discarded). What results is a liquid rich in gelatin, which in some cases may be drunk right away as a nutrient-rich bone broth. In commercial food processing, this liquid is refined further through a series of evaporation and milling techniques to create gelatin powder or sheets, which is then sold as a food additive most commonly known as Jell-O. This process is known as partial hydrolysis.
For those of us looking to boost collagen production in our own bodies for health and beauty benefits, however, it's better to seek out collagen in peptide form. Collagen peptide supplements and products contain collagen that has been fully hydrolyzed into nano-sized particles called collagen peptides.
Fully hydrolyzed collagen (collagen hydrolysate) has the ability to reach your bloodstream intact, where it can trigger your fibroblasts to produce more collagen.
4 Ways to Support Collagen Synthesis
So if you want to help your body produce more collagen, here are our expert tips on the best ways to do just that:
1. Collagen Supplements
The best way to increase collagen production is with collagen supplementation. Period. Because a good quality collagen supplement is expertly formulated with hydrolyzed collagen peptides, you can trust that it will reach your bloodstream and trigger collagen production right away.
Taut Liquid Collagen is a supplement you can rely on. Here's why every sip of our anti-aging beauty booster really works:
- It's packed with premium marine-sourced collagen, the best type for healthy skin.
- Every bottle contains a high dose (13,000 mg) of collagen peptides, properly hydrolyzed for maximum absorption.
- It contains a selection of skin-loving ingredients: elastin, hyaluronic acid, vitamins C and B6, grape seed extract, ceramide, and salmon DNA to repair, protect, and brighten your skin.
A daily dose of our premium collagen supplements triggers collagen production in your fibroblasts, contributing new collagenous fibers to your dermis that improve skin strength, thickness, and smoothness – for a younger-looking, more radiant you!
2. Foods
It really is true that healthy eating can have a big impact on your skin, and you can certainly tailor your diet to improve the amount of collagen made in your body.
Because collagen is found mainly in the skins, cartilage, bones, and eyes of meat and fish, it doesn't make for the most appetizing menu. If you don't fancy chewing on fish skin or eyeballs, the good news is that there are other ways to make your diet more collagen-friendly.
When it comes to collagen foods, you could try some gelatin-rich bone broth, which is rich in type 2 collagen and is particularly good for your joint health. Organ meats like liver and kidneys are also rich in collagen – although they're not to everyone's tastes!
The good news is that you can also support your body's collagen production with foods rich in the amino acids, vitamins, and minerals that build this essential protein.
Get an amino acid boost from red meats, poultry, and fish. Seeds, nuts, tofu, and eggs are also rich in glycine, and you can get proline from dairy products, asparagus, and mushrooms. Pack your plate with leafy greens, bell peppers, and citrus fruits to stock up on vitamin C. Whole grains, beans, and nuts are rich in zinc, while spirulina, sweet potatoes, and dark chocolate are rich in copper.
Together, the above foods can help provide your body with the essential building blocks for collagen synthesis.

3. Skincare Products
Aside from foods and supplements, there are a number of topical skincare treatments that can help boost collagen production in the dermis.
So what should you look out for on your skincare labels? Aside from collagen peptides, the best ingredients to boost collagen production are:
- Retinol – a vitamin A derivative that boosts skin cell turnover
- Vitamin C – an essential cofactor of collagen, and a potent antioxidant to boot
- Hydroxy acids – exfoliating acids often referred to as AHAs or BHAs
- Hyaluronic acid – a hydrating, skin-plumping acid that supports collagen in the dermis
- Growth factors – cell-signaling factors that trigger collagen synthesis
With Taut Collagen Mask, you can boost collagen production for a younger-looking complexion in one 15-minute treatment. Our luxurious formula is packed with our hydrolyzed collagen peptides, which are easily absorbed into the dermis where they can get to work straight away.
These sheet masks are infused with a luxurious essence rich in vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, and botanical squalene. Vitamin C acts as an essential cofactor for collagen synthesis, grape seed extract is a potent antioxidant that protects and brightens your complexion, and hyaluronic acid hydrates and plumps for a smoother, softer skin texture.
Consider it your go-to treatment for reducing fine lines, maximizing radiance, and seriously plumping up your skin. Ready, set, glow!
4. Skincare Treatments
There are a number of treatments out there that can go one step further than your day-to-day skincare routine to make more collagen in your dermis. These include:
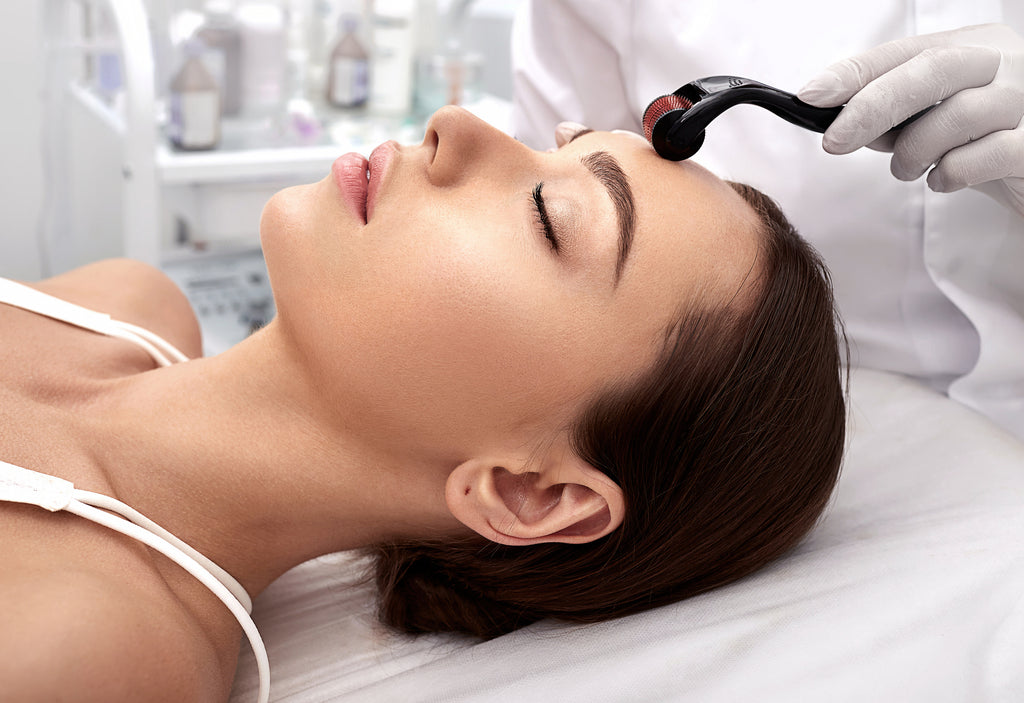
- Microneedling or Dermarolling – at-home and professional treatments that use a needle-covered roller device to create pin-prick wounds on your skin, triggering your fibroblasts to produce collagen.
- LED Red Light Therapy – uses infrared light to penetrate to the dermis, where heat and light waves activate your fibroblasts and create more collagen.
- Collagen Injections – fillers and injections that are used to reduce lines and deep-set wrinkles.
If you're keen on boosting your collagen with a more in-depth treatment, visit your dermatologist for a face-to-face consultation to discuss your options.
Don't Forget to Avoid Collagen Destroyers
While you're here, we can't forget to remind you that it's also extremely important to avoid things that damage collagen in your body. If you're trying to boost your body's collagen production process, try to avoid sugar (candy, soda, refined carbs), alcohol, cigarette smoking, and excessive sun exposure as these can all damage your existing collagen and cause premature aging.
Transform Your Skin with Taut
If you want to support the natural ways in which collagen is made in your body, you can do so with a healthy diet and some high-quality collagen supplementation.
Here at Taut, we truly believe that healthy skin starts from within, and that's why we created the Intense Transformation Program. This program is the cornerstone of our premium skincare products, offering you the optimum supply of Taut Liquid Collagen – one bottle per day for three weeks – to help you get your skin back on track. With our expert collagen peptide formula packed with skin-loving ingredients, the Intense Transformation Program sets you on the right path to firmer, fuller, smoother, more radiant skin, and visibly reduced fine lines and wrinkles.
Like what you see? Subscribe to our auto-ship service & enjoy up to 15% off your transformation program here.
References: