Collagen Definition: We Define Collagen & the Anatomy of This Protein

Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It is a family of fibrous proteins in mammals. You'll also see the word labeled on many of the best skin care products and supplements. If you're wondering what exactly is collagen, then we've got the guide for you!
Keep reading to find out what is collagen, what does it do, and how can you use it as an ingredient to boost your health and wellbeing.
Definition of Collagen
Collagen (noun): A family of fibrous proteins in humans and animals that forms the structure of connective tissue, skin, bones, joints, tendons, and teeth.
What Is Collagen?
Let's expand on what collagen really is, beyond the dictionary definition.
Collagen is a type of protein that exists in humans and other mammals. It is a fibrous protein that forms a structural foundation for many of your organs and tissues, most notably your bones, skin, joints, connective tissue, and muscles. Collagen ranges in elasticity depending on where in the body it is found. Some types of collagen fibers are rigid (e.g. in bones), while others are more flexible (e.g. in tendons).
The name collagen comes from the Greek word 'kólla', which means glue. This name is pretty apt, as it functions like a glue that holds our bodies together.
To define collagen, it's best to consider it in two ways: collagen as it is made in the body and collagen as an ingredient in skincare or collagen supplements. These can both be described as "collagen" but the former is a substance that is formed naturally within the body, and the latter is derived from animal or marine sources in order to be digested by the human body to boost collagen production.
Collagen in Your Body
First up, we'll explain the collagen that you have in your body. Collagen is the main and most abundant protein in your body, making up approximately 30% of your whole-body protein content. It forms much of the basis of your skin, joint cartilage, connective tissue, muscles, blood vessels, and more.
Collagen lives in what's known as an extracellular matrix, which is a network of cells, proteins, and other molecules that gives structure to a number of connective tissues in the body.
Although it sounds like a singular term and is often described as one thing, collagen is actually a family of proteins. There are 28 types of collagen that are currently known and studied, each having a different role in the body. Luckily for us, there are really only five types that we really need to know about:
Type I Collagen
Type I is number one for a reason – it makes up between 80-90% of the collagen in your body. Type I collagen fibrils are found in your skin, bones, tendons, cartilage, connective tissues, teeth, hair, and nails. Collagen type I is also needed for cell migration, tissue remodeling, and wound healing.
When people take collagen supplements for anti-aging purposes, it's likely that these products contain type I collagen. This is because the decline of your natural collagen level, particularly type I collagen, is a major factor in skin aging, leading to often-unwanted wrinkles and sagging.
Type II Collagen
Type II collagen is a major component of your cartilage, bones, and connective tissue, making it a key player in the health of your joints. This type is made of more loosely-packed fibers than type I, lending it a more compliant, flexible, and shock-absorbing structure that helps cushion your joints.
Collagen type II works alongside elastin, proteoglycans, and hyaluronic acid to form the structure of your joint tissue. Where it is most important is the articular cartilage, which is the dense connective tissue that cushions the ends of your bones and prevents friction at the joints. Here, type II collagen forms 90% of the tissue structure. 2
If you hear of people taking collagen supplements for joint health, it's likely a type 2 supplement.
Type III Collagen
Type III collagen is found in your muscles, arteries, bone marrow, and organs. It typically exists alongside type I collagen as a supporting mesh-like structure known as reticular fiber.
Type IV Collagen
Type IV collagen is a little different from the other types we've looked at so far, as it is non-fibrillar. This means that it is composed of short-chain collagens that don't form into a collagen fiber.
This type is important in what's known as basement membranes, which are the lower layers of the skin and other tissues. These membranes are responsible for filtration, keeping harmful cells and substances away from deeper tissues.
Type V Collagen
Last but not least, type V is fibrous collagen that contributes to the structure of your hair, cell surfaces, and placenta.
Collagen Synthesis: How Collagen Is Made
A collagen molecule is made up of amino acid chains that have been twisted into what's known as a triple helix structure. This process is called collagen synthesis.
This synthesis process happens in the extracellular matrix, which is a web-like network of cells, proteins, and molecules in your body. It's basically a foundational layer for your tissues.
Within the extracellular matrix, you have some specialized cells called fibroblasts, which are the cells responsible for making collagen. They combine amino acids into chains, which are then linked together into a triple helix structure. This all happens within the fibroblast.
Your fibroblast cells then secrete these chains out into the extracellular matrix, where they bond together to create collagen fibrils. These collagen fibrils then come together again to create more robust collagen fibers, which are the sturdy protein structures that can support your skin, joints, connective tissue, muscles, and more!
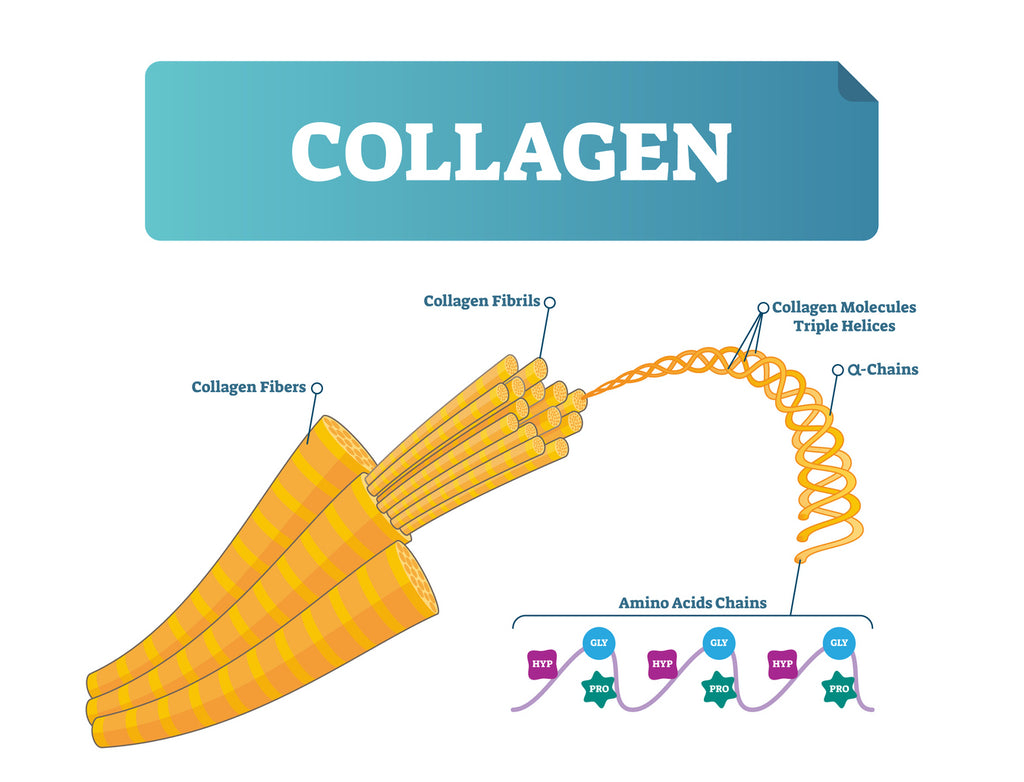
Collagen Structure: What Are Collagen Molecules Made of?
Let's take a closer look at the elements your body needs to create a collagen molecule:
Amino Acids
Your body needs two amino acids to produce collagen protein molecules: glycine and proline. These amino acids are elements in the synthesis of many different proteins. Collagen production sometimes also involves the amino acid lysine.
Like all proteins, collagen is made up of polypeptide chains, which is when three amino acids come together in a chain that is linked by peptide bonds. In collagen, the sequence of amino acids in this chain is glycine, proline, then either hydroxyproline or hydroxylysine (which are oxidized forms of proline and lysine, respectively). These polypeptide chains can also be called alpha peptides.
When three of these polypeptide chains come together, they form a triple helix – which is collagen's unique molecular structure.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is what's known as a cofactor in collagen production. Unlike amino acids, it's not in the triple helical structure itself, but it causes a chemical reaction that is crucial to turning those polypeptide chains into a triple helix.
Turning alpha peptides into a triple helix requires an enzymatic reaction, in which the enzymes prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase can convert proline or lysine into hydroxyproline or hydroxylysine, respectively.
This may sound complex, but don't worry, you don't really need to remember the names of all those enzymes! The most important thing you need to know is that vitamin C, otherwise known as ascorbic acid, is what's needed to activate those enzymes. When vitamin C activates those enzymes, the polypeptide chains are able to bond together to form the super helix.
Zinc & Copper
Zinc and copper are two minerals that are needed to complete collagen formation. Copper works with vitamin C to activate the enzymes mentioned above and create the collagen fibril, while zinc protects your fibroblast cells from harm during the synthesis process.
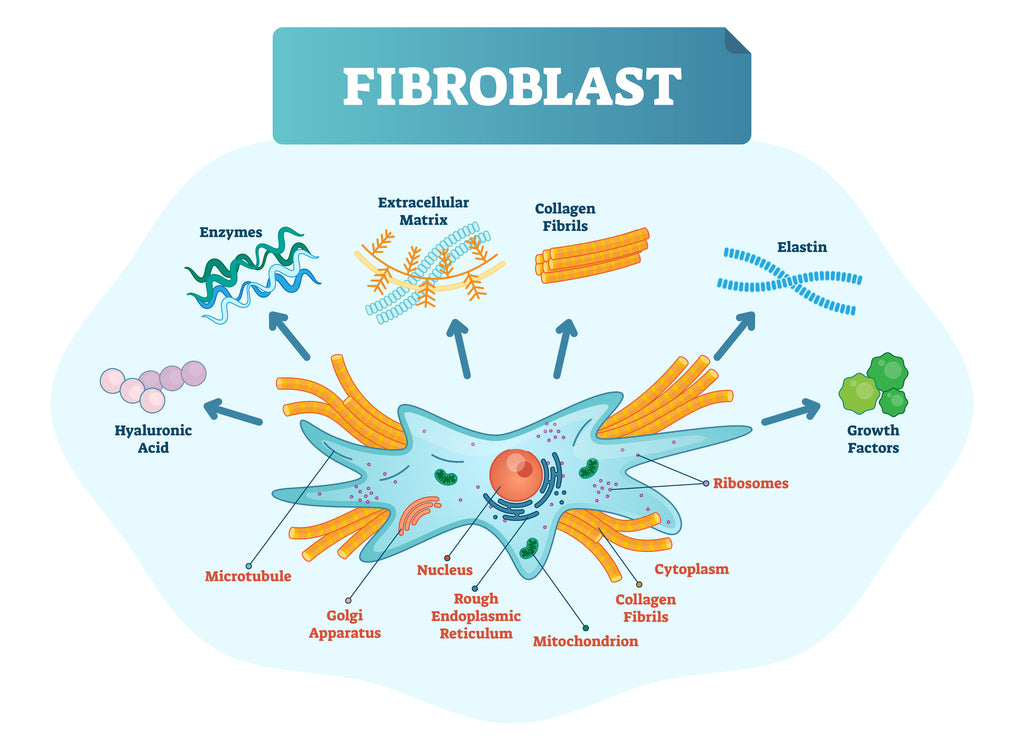
What Does Collagen Do?
Now that we have a basic understanding of what collagen is and what it is made from, let's discover why this protein is so important! Here's how collagen benefits your body:
Maintains Skin Elasticity, Thickness & Strength
You'll find it in anti-aging skin care products and supplements for this reason – collagen is the protein responsible for keeping your skin smooth, supple, and wrinkle-free.
Collagen, specifically type I collagen, is the main component of the dermis, which is the lower layer of your skin that sits below the surface layer (epidermis). Your dermis is packed with a network of collagen fibrils and fibers that are strong enough to keep everything in place, yet flexible enough to give your skin some stretch.
Collagen works in the dermis alongside elastin, a stretchy protein that boosts your skin elasticity; and hyaluronic acid, a water-binding molecule that makes skin plump and soft.
Collagen is responsible for your skin strength, which in turn impacts how young, smooth, and radiant your complexion is. Young people have a healthy and plentiful supply of collagen because the body makes it naturally and quickly at a young age. This is why youthful skin is so enviably smooth and firm. As we get older and experience collagen loss, both in quantity and quality, our skin begins to thin, wrinkle, and sag.

Assists Wound Healing
You may have noticed that wounds heal a little bit slower as you get older, and part of this is thanks to a reduction of collagen in your body.
Collagen plays an important role in the wound healing process. When you get a scrape or a cut, your body sends a message to your fibroblasts that more of this essential proteion is needed.
Collagen functions to stop bleeding and draw cells in from your immune system to the site of the wound. It also increases the rate at which new blood vessels are made beneath the dermis, which helps the growth of new tissues and slows down the spread of harmful bacteria. 4
Lastly, collagen also has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce swelling and pain and speed up healing at the site of the wound.
This all comes together to create the right environment for wounds to heal quickly, without the risk of infection.
Strengthens Connective Tissue & Joints
Because collagen makes up so much of the microfibrillar structure of cartilage and tendons, particularly the articular cartilage where your bones meet, it plays a big part in how healthy and strong your joints are. By keeping cartilage strong and stable, collagen keeps your joints limber and enables your ease of movement on a daily basis!
When collagen levels decline, our joints become weaker. Hence why we are more prone to aches and stiffness in our wrists, knees, elbows, and ankles as we get older.
Without a healthy supply of this protein, we can become more prone to arthritic conditions that cause pain, inflammation, stiffness, and tenderness in the joints.
Creates Muscle Tissue
We all know that protein is important for our muscles, and it's no less true when it comes to collagen.
Collagen forms between 1–10% of your muscle tissue, making it an important component for your strength and ability to move throughout the day. Having healthy, strong muscles also aids your overall joint health.
This protein is also important in muscle repair, and it is one of the elements that aid recovery after a workout or a muscular injury. In fact, studies suggest that taking collagen supplements can significantly improve muscle growth and repair after a workout.

Maintains Bone Density
It's true that calcium is a key ingredient for bone health, but did you know that the second most important nutrient is collagen? That's right, these fibrous proteins are absolutely essential to bone health!
While calcium is a key component in the hard outer shell of a bone, collagen makes up a large portion (around 90%) of the softer bone marrow within. This protein plays an important role in your bone mineral density (BMD), which is a scale that is used to measure the overall health and strength of your bones. A low BMD can be linked to bone disorders such as osteoporosis.
Having a healthy supply of natural collagen keeps your bones strong, and helps prevent bone loss.
Improves Circulation & Heart Health
Collagen is also a key element in the structure of your arteries and blood vessels, which are key to healthy circulation and regulated blood pressure. This makes it a key element in your overall heart health.
In fact, studies suggest that collagen may help lower the amount of bad cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), which helps prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries and reduces the risk of heart disease. 7
Contributes to Strong Hair & Nails
Last but not least, this superstar protein also contributes to the health and strength of your hair and nails!
Because collagen is such an important part of the dermis i.e. your skin, it is also a key player in the health of your scalp and hair follicles. Collagen surrounds each new hair that grows from your head, contributing to a healthy rate of growth and strong, luscious hair.
Collagen's role in maintaining healthy circulation also stimulates hair and nail growth. Without it, your hair may begin to thin and your nails may break more easily.

Why Do We Lose Collagen?
Collagen is the main component in so many aspects of our body's structure, and therefore it is essential to our health and wellbeing. Many health and beauty concerns can be linked back to a decline in the quantity and quality of the collagen in our bodies, but why does this happen?
Defects in collagen can lead to conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, a group of disorders affecting connective tissue. Deficiencies or mutations in collagen can lead to conditions such as osteogenesis imperfecta, a disorder characterized by fragile bones.
There are a number of factors that contribute to a decline in our collagen supplies. Let's take a look at the main and most important reasons this happens:
Age
The main, unavoidable reason we lose some of the collagen in our bodies is the intrinsic aging process, a.k.a. the passing of time. Unfortunately, there's no avoiding this one!
When we are young, our bodies will produce a large number of high-quality collagen proteins, quickly and easily. This is why babies have such soft, plump skin, and why our skin, hair, nails, and joints are so healthy in our youth.
When we get older, our cells age and they begin to produce lower quality collagen, and less of it. This degradation of our vital supplies leads to a loss of skin elasticity, wrinkles, sagging skin, slower healing of wounds, stiffer joints, and weaker bones – to name just a few.
For women, this decline is made worse by menopause, which brings a hormonal shift that drastically impacts the body's ability to produce collagen. In fact, most women will lose around a third of their collagen supplies during the first five years of menopause.
Exposure to the Sun
When it comes to maintaining the collagen in your dermis, it's absolutely essential that you protect your skin from the sun's harmful UVA and UVB rays.
UVA rays are extremely harmful to your collagen supplies, as they penetrate deep into the dermis and cause an abnormal buildup of elastin, which in turn produces enzymes that break down protein structures. In fact, UVA radiation can a higher rate of collagen breakdown than chronological aging. That's a big deal!
This is why it is so important to keep our skin protected from the sun with good quality SPF lotions and protective clothing. If we don't protect ourselves, we will be much more prone to collagen degradation which leads to more severe wrinkles, sagging, and age spots.
Poor Diet
If you want to protect your collagen, the choices you make in the kitchen and at the grocery store are oh-so-important. And when it comes to making food choices, you should know that sugar is, unfortunately, public enemy number one.
Not only is sugar literally addictive, but it also causes blood sugar spikes in your body that can lead to health problems and (you guessed it) collagen degradation.
When we consume sugary or highly processed foods, our blood sugar goes up and something called glycation happens.
Glycation is when glucose attaches to proteins in your bloodstream and produces free radicals called advanced glycation end products. These advanced glycation end products attack and weaken the microfibrillar structure, and your precious collagen starts to disintegrate.
This is why it's so important to keep an eye on our sugar intake, watch out for sneaky added sugars in processed foods, and cut back on junk food, boosting our intake of fiber, protein, and healthy fats instead.
Smoking Cigarettes
Not only can smoking lead to some scary health conditions, but it also causes damage to our collagen which in turn impacts our skin health. Cigarette smoke is packed with over 4000 chemicals, many of which attack your body's collagen and elastin proteins.
This causes significant damage to the structural foundations of your dermis, and it's why smokers are much more likely to look older than their non-smoking counterparts. One study proved this by examining identical twins, one of whom smoked cigarettes daily, and the other who didn't smoke. Unsurprisingly, the results proved that smokers had much more wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, and sagging that made them look older and unhealthier. 9 
Drinking Alcohol
Although a casual glass of wine at the end of a long week of work isn't the end of the world, drinking alcohol in excess can be harmful to your collagen supplies.
Alcohol is technically a toxin, and when we drink it enters the bloodstream and creates chemicals that the liver recognizes as toxic and needs to flush out. This process also flushes water and salt from your body, and it causes inflammation and free radical damage that breaks down the collagen and elastin in the body.
Collagen in Supplements & Products
We have covered the definition of collagen as it is found in the human body, identifying what it does and how it can be damaged with time and exposure to harmful substances. Now we can move on to the second definition of "collagen", this time covering this protein as it is found in supplements and health and beauty products.
In this section, we will cover where this collagen comes from, what forms it can take, and how it works.
External Sources of Collagen
Collagen is not only found in the human body, it can also be found in animals and marine life. Let's take a closer look:
Marine Collagen
Marine collagen comes from sea life. It is typically derived from fish skin, connective tissue, and scales of cold sea fish such as snapper, salmon, or cod.
It is one of the richest sources of type I collagen, which is the type we need for strong, smooth, and youthful-looking skin. This makes it the number one choice for beauty and anti-aging supplements.
It's also loved by beauty supplements for its high bioavailability, which means that it can be quickly and easily digested and used by the body once taken. The higher the bioavailability, the better the supplement!
Taut Liquid Collagen is a premium drink made with highly bioavailable marine collagen peptides, designed to revamp your skin with fast, visible, and long-lasting results.
Our formula is packed with 13,000 mg of marine collagen peptides along with elastin peptides, hyaluronic acid, grape seed extract, vitamins C and B, ceramide, and salmon DNA. Think of it as the skin-loving dream team that can transform the quality and texture of your skin from the inside out!
When you drink a bottle of Taut Liquid Collagen, you are giving your body the nutrients it needs to replenish that essential collagen network in your dermis, making up for lost collagen and reducing the signs of aging on your skin. Antioxidants and hydrating ingredients come into the equation to maximize skin smoothness and radiance, giving you that enviable youthful glow!
Animal Collagen
Animals are another source of collagen for supplements and skincare products, the most common types being:
- Bovine collagen – extracted from the hides, bones, and cartilage of cows
- Porcine collagen – extracted from the bones, cartilage, and knuckles of pigs
- Chicken collagen – extracted mainly from chicken cartilage
Collagen from other animals is less common. Many supplements will either contain bovine collagen or a mix of bovine, porcine, and chicken collagens.
Animal collagen can contain a mix of collagen types I, II, and III. It has a slightly lower bioavailability than marine collagen, as it has a larger molecular structure. In fact, research suggests that marine collagen absorbs up to 1.5 times faster than animal collagen. 10
Bovine collagen can make a great supplement for muscular health, and chicken collagen is especially good for your joints. When it comes to skin health, there are bovine supplements that can help improve the collagen in your dermis, however, we believe that marine collagen is the better choice thanks to its bioavailability, sustainability, and high concentration of type I collagen.
Types of Collagen Supplements & Products
So where does this type of collagen typically show up? There is a range of different supplements out there, from collagen powders and pills to liquid collagen drinks. These supplements can be made in a number of ways, with each format having a slightly different impact on your body. Let us explain:
1. Undenatured Collagen
If you see "undenatured" or "native" on the label, this is a supplement that contains collagen molecules in their entirety. The collagen has not been processed or broken down into peptides or specific amino acids, so it still has its triple helix structure.
This type of collagen is designed to be ingested, bypass the digestive system and reach your small intestine intact. Here, it can interact with your immune system through the lymph follicles, where it serves a specifically anti-inflammatory purpose. It helps to train your immune system not to attack its own collagen supplies, which is crucial in treating specific autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Undenatured collagen should not be confused with gelatin or a hydrolyzed supplement, and it is not used for skin or muscle health.

2. Gelatin
Gelatin is a form of collagen that has been partially denatured i.e. broken down. Gelatin is made by boiling down the bones, skins, and connective tissue of animals and fish, which is a process that extracts the natural collagen and breaks it down into smaller, more digestible amino acids.
Gelatin is commonly used as a food additive thanks to its high gel strength, which is useful for bakers and in your bowl of Jell-O! However, gelatin can also be found in dietary supplements that help boost your body's ability to produce collagen.
You'll also find gelatin occurs naturally in some foods. Because boiling bones, connective tissue, and cartilage in water yields gelatin, bone broth is a soup that can have collagen-boosting benefits for your body. Bone broth can help provide your body with the specific amino acids needed to make more collagen, although it is primarily going to help your body make type 2 collagen, a key ingredient in healthy joints but less beneficial for your complexion than a hydrolyzed supplement.

3. Hydrolyzed Collagen
Hydrolyzed collagen supplements are the most common and effective type of collagen supplement out there, and they may be found in the form of liquid collagen drinks, collagen powders, and collagen pills.
When you digest this type of supplement, the peptides enter your bloodstream and trigger your fibroblasts to speed up the collagen production process, which in turn strengthens your dermis and other key connective tissue in the body.
This type of supplement is made by breaking down collagen molecules into nano-sized pieces called peptides through a process called hydrolysis. This process is designed to make collagen as digestible as possible, so your body can absorb it very quickly and use it straight away.
All of Taut's collagen products use hydrolyzed peptides from premium marine sources, and Taut Collagen Powder is no exception. A lighter dose than our liquid drink, Taut Collagen Powder contains 1500 mg of collagen peptides in each sachet, designed to be taken on the go.
Because our collagen powder doesn't need refrigeration, you can pack it in your purse or in your car and always have a premium collagen supplement close by. Taut's premium formula combines collagen peptides with grape seed extract and hyaluronic acid, for a triple action beauty booster that hydrates, protects, and repairs your skin!
4. Topical Collagen
You'll also find collagen in a variety of topical treatments, which will generally contain collagen peptides. This is because anything larger than a properly hydrolyzed peptide is unlikely to be properly absorbed by the skin and into the dermis.
Topical collagen treatments are a great way to tackle your skin concerns, as they specifically target the dermis. Taut Collagen Mask is our topical solution to any dullness, fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging you may be experiencing. These are some of the typical skin concerns that crop up as we get older and our collagen supplies begin to fade, so we created this luxurious sheet mask treatment to combat those pesky signs of aging.
Infused with an essence packed with hydrolyzed marine collagen peptides, vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, and botanical squalene, this face mask has a seriously hydrating and skin-plumping effect. Just apply and relax for 15 minutes while the mask gets to work. It's the perfect way to bring the spa experience home and get some well-deserved you time!
Summary: Collagen Defined
Collagen (noun) is a family of fibrous proteins that make up the majority of your skin, joints, muscles, and connective tissue. It's a major component of your skin that keeps your complexion young and radiant.
Collagen supplements and topical collagen treatments are derivatives of marine and animal collagens that we use to boost our natural collagen production process.
The Best Way to Boost Your Collagen Inside & Out
If you want to boost your collagen production and improve your skin health, look no further than our Ultimate Transformation Program. This little beauty bundle contains a three-week supply of our signature liquid collagen, a pack of five collagen masks, and a box of Taut Hydrate, our beauty supplements that hydrate your skin from the inside out.
Together, the components of this kit boost your collagen from within and at the surface level. Our liquid drink maximizes your internal collagen synthesis process, while our luxurious sheet mask fights collagen loss from the outside in. To top it all off, Taut Hydrate offers an added boost of hyaluronic acid to maximize plumpness and smoothness – helping rid your skin of fine lines and imperfections.
It really is the ultimate program for fighting the signs of aging!
Did you know you can save up to 15% on your transformation program if you subscribe to our auto-ship service?
References:
- The Collagen Family
- The Basic Science of Articular Cartilage
- Influence of zinc on synthesis and the accumulation of collagen in early granulation tissue
- Collagen effective in wound closure
- Collagen in Wound Healing
- Collagen peptide supplementation
- Effect of Collagen Tripeptide on Atherosclerosis in Healthy Humans
- Caring for your skin in menopause
- Twins, smoking and mortality
- Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources